Microcaptives, also known as captive insurance companies, have been gaining significant attention in recent years for their potential to offer unique advantages and benefits. In particular, the IRS Section 831(b) tax code has created a framework that enables businesses to establish microcaptives and take advantage of the various insurance benefits they can provide. By navigating this innovative approach, companies can not only gain more control over their insurance coverage but also potentially enjoy tax advantages.
Captive insurance, in its essence, involves a strategy where a business establishes its own insurance company to provide coverage for its own risks. This captive insurance company, known as a microcaptive when it meets the requirements of the 831(b) tax code, operates under a different set of rules compared to traditional insurance providers. The primary distinction lies in the ability of the microcaptive to qualify for certain tax benefits and deductions.
Under the IRS Section 831(b) tax code, microcaptives that meet specific criteria can elect to be taxed only on their investment income, instead of on their premium income. This approach can result in potential tax savings for businesses, making it an attractive option for many. Furthermore, by forming a microcaptive, companies gain greater control over their insurance programs, allowing them to tailor coverage to their specific needs and potentially gain access to additional sources of capital.
Overall, the concept of microcaptives presents intriguing possibilities for businesses seeking to optimize their insurance strategies. By understanding and leveraging the advantages offered by the IRS 831(b) tax code, companies can unlock new potentials, maximize their insurance benefits, and gain a competitive edge in managing their risks and financial portfolios.
Understanding Microcaptives: What They Are and How They Work
Microcaptives, sometimes referred to as 831(b) captives, are a type of insurance company that provide a unique risk management solution for businesses. These captives operate under the guidelines of the IRS 831(b) tax code, which allows small- to medium-sized businesses to form their own insurance companies to cover specific risks.
By forming a microcaptive, businesses can gain more control over their insurance coverage and potentially maximize their insurance benefits. Instead of relying solely on traditional insurance providers, businesses can create their own captive insurance company to insure against certain risks that may be difficult to cover through traditional means.
The process of establishing a microcaptive involves creating a separate legal entity that acts as the insurance company. This entity is owned by the business or business owner and is funded by the premiums paid by the insured parties. The microcaptive then assumes the risks of these insured parties and provides them with insurance coverage.
One of the key benefits of a microcaptive is the potential for tax advantages. Under the IRS 831(b) tax code, microcaptives are eligible for certain tax benefits, such as the ability to exclude a certain amount of premiums from taxable income. This can result in significant tax savings for businesses.
In conclusion, microcaptives offer businesses the opportunity to take control of their insurance coverage, potentially maximize their insurance benefits, and access tax advantages through the IRS 831(b) tax code. Understanding how these captives work and the benefits they provide can help businesses make informed decisions when it comes to managing their risks and protecting their assets.
The Benefits of Utilizing the 831b Tax Code for Captive Insurance
The 831b tax code provides significant advantages for businesses looking to establish a captive insurance company. With its specific provisions, this tax code allows small to mid-sized businesses to enjoy enhanced insurance benefits and potential cost savings.
One key benefit of utilizing the 831b tax code is the ability to generate substantial tax savings. By electing to be taxed under this provision, businesses can receive favorable tax treatment on the income generated by their captive insurance company. This means that premiums paid to the captive can be deducted as ordinary and necessary business expenses, reducing the overall taxable income of the parent company.
Another advantage of the 831b tax code is the potential for a more tailored insurance program. By establishing a captive insurance company, businesses have the ability to customize coverage specific to their unique risks and needs. This allows for greater flexibility in designing insurance policies that align precisely with the organization’s risk management goals.
In addition to these benefits, utilizing the 831b tax code can also provide businesses with better control over their insurance costs. With a captive insurance company in place, businesses have the opportunity to retain the underwriting profits and investment income that would typically go to traditional insurance carriers. This can result in long-term cost savings and potentially improved cash flows, as the captive insurance company becomes a valuable asset for the business.
In conclusion, taking advantage of the 831b tax code for captive insurance offers businesses numerous benefits, including tax savings, tailored insurance programs, and increased control over insurance costs. By understanding and leveraging these advantages, businesses can unlock the full potential of microcaptives and maximize their insurance benefits.
Maximizing Insurance Benefits with Microcaptives: Strategies and Best Practices
Microcaptive
In order to unlock the full potential of microcaptives and maximize insurance benefits, it is important to implement effective strategies and best practices. By doing so, businesses can take advantage of the unique opportunities offered by microcaptives while ensuring compliance with IRS 831(b) tax code regulations.
Proper Evaluation and Risk Assessment: Before establishing a microcaptive, conducting a thorough evaluation and risk assessment is crucial. This involves identifying and quantifying the risks faced by the business, considering both insurable and non-insurable risks. By understanding the specific risks involved, businesses can tailor their microcaptive policies to provide optimal coverage.
Careful Selection of a Captive Manager: Choosing the right captive manager is another critical step. It is important to select a manager with expertise in microcaptive formations, IRS 831(b) compliance, and ongoing management. A reputable manager will ensure that the microcaptive is structured and operated appropriately, helping businesses achieve tax benefits while mitigating potential regulatory issues.
Strategic Underwriting and Risk Pooling: Effective underwriting practices are key to maximizing insurance benefits with microcaptives. Businesses should strive to write meaningful and diversified policies to provide coverage for a broad range of potential losses. By pooling risks from multiple insured entities within the microcaptive, businesses can increase the stability of the insurance arrangement and enhance the overall risk management strategy.
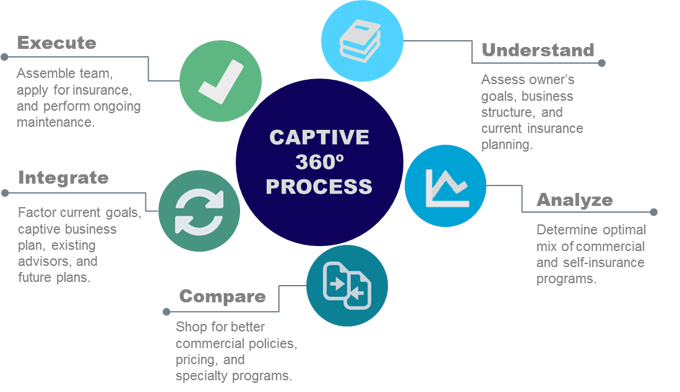
By following these strategies and best practices, businesses can fully unlock the potential of microcaptives and reap the maximum insurance benefits available. However, it is important to remain informed about the ever-evolving IRS 831(b) tax code regulations to ensure ongoing compliance and to adapt strategies accordingly.






Recent Comments